Copyright ©2017 all rights reserved
Designed by Plethora Themes
Developing Main Group C-H Bond-breaking Tools: Complementary Strategies to Directed ortho-Metalation
University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK
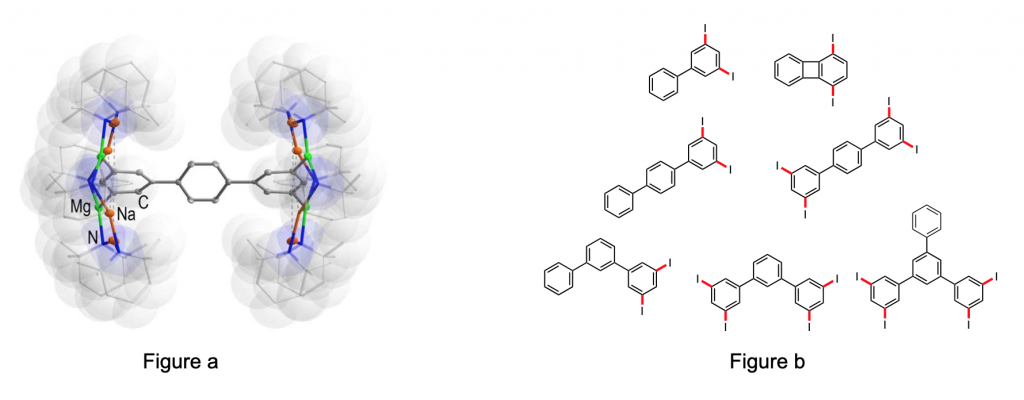
To date the seminal metalation strategy employed in synthesis has been Directed ortho-Metalation (DoM). The first example of DoM was reported as long ago as 1938/9,1,2 and this discovery propelled organometallic compounds from being exotic rarities to indispensable tools in modern synthesis.3 While there have been a number of reports of metalation at more remote sites, in general these reactions operate in the same way as DoM, namely that the position of metalation is controlled by the substituent attached to the aromatic ring. In our new template approach, which involves using a sodium magnesiate reagent [Na4Mg2(TMP)6nBu2] 1 (TMP = 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidide) which can be prepared in an easy manner, it is primarily the positions of the metal centers within the template ring that control the positional metalation reactions. In this presentation, our recent results using 1 to perform regioselective metalations will be discussed, culminating in Directed ortho–metaʹ- and meta–metaʹ-dimetalations.4 We have also shown that polyarenes can be metalated (Figure a) and after quenching with iodine it is possible to generate hitherto unknown simple iodoarenes (Figure b), which have potential for use in materials and pharmaceutical applications. Other examples of the versatility of the template base approach to metalation will also be revealed.
References:
(1) H. Gilman, R. L. Bebb, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 109-112.
(2) G. Wittig, U. Pockels, H. Droge, Ber. Deutsch. Chem. Gesel. 1938, 71, 1903-1912.
(3) M. Schlosser, Organometallics in Synthesis Third Manual. (Ed. M. Schlosser), John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey, 2013.
(4) A. J. Martínez-Martínez, A. R. Kennedy, R. E. Mulvey, C. T. O’Hara, Science, 2014, 346, 834-837.
(5) A. J. Martínez-Martínez, S. Justice, B. J. Fleming, A. R. Kennedy, I. D. H. Oswald, C. T. O’Hara, Science Advances, 2017, e1700832.